Navigating the world of patents can feel like a daunting task, especially if you’re new to the concept. However, understanding patents is crucial for inventors, businesses, and even curious individuals who want to protect their innovations. This guide aims to demystify patents and provide a clear overview of what they are and how they function within the realm of intellectual property law. So, what is a patent?
At its core, a patent is a form of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a certain period, typically 20 years. In exchange, the inventor must publicly disclose the details of the invention. This trade-off encourages innovation by allowing inventors to potentially profit from their creations while contributing to the collective knowledge pool.
Types of Patents
There are three main types of patents that cover different kinds of rights:
Utility Patents
Utility patents are the most common type and are granted for new and useful processes, machines, articles of manufacture, or compositions of matter. They focus on the functional aspects of an invention, such as how it works.
Design Patents
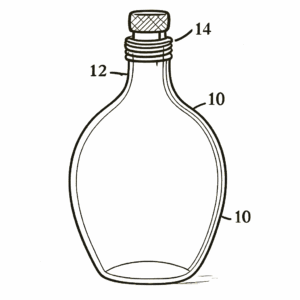
Design patents protect the ornamental design of a functional item. They do not cover the item’s utility but rather its aesthetic features. For instance, the unique shape of a perfume bottle can be protected by a design patent. Design patents have different names in other jurisdictions and may be referred to as industrial designs or registered designs.
Plant Patents
Plant patents are relatively rare and are granted to inventors who discover or invent a new and distinct variety of plant. This category covers plants that have been asexually reproduced.
The Patent Application Process
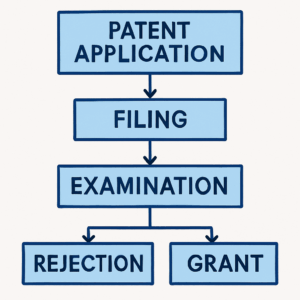
Understanding the patent application process is essential for securing a patent. The process typically involves several steps:
– Research: Before applying for a patent, conduct a thorough search to ensure your invention is novel and has not been patented by someone else.
– Drafting: Prepare a detailed patent application that includes specifications, claims, and drawings of your invention.
Filing: Submit the application to the relevant patent office, such as the UK Intellectual Property Office for the UK (UKIPO) and the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) for the US.
– Examination: The patent office will examine the application to determine if it meets the necessary criteria for patentability.
– Approval: If the application is approved, the patent is granted, and the inventor gains exclusive rights to the invention for up to 20 years from filing.
Patent Law and Its Importance
Patent law plays a vital role in protecting inventors’ rights while promoting innovation and competition. By safeguarding inventions, patent law encourages inventors to share their creations with the public, advancing technology and society as a whole.
Understanding patents and patent law is crucial for anyone involved in innovation, whether you’re an inventor, a business owner, or just someone interested in how the world of intellectual property works. With this knowledge, you can better navigate the complexities of protecting and leveraging your inventions.





